Eustachian Tube Dysfunction Treatments
The Eustachian Tube (ET) controls air pressure relief inside what is called the middle ear (behind the eardrum where all the fancy ear stuff happens). This area behind the eardrum is a mostly closed off small space that is prone to pressure accumulation. Building of pressure happens in the ear naturally after just a few minutes, but the body normally relieves this pressure by quickly opening the ET and allowing airflow to happen and pressure to equalize. In severe problems the ET never opens well because it may be simply too small, too stiff, or scarred shut. These patients will have problems with fluid accumulation in the ears, ear infections, and often holes that develop in the eardrum to relieve the pressure otherwise.
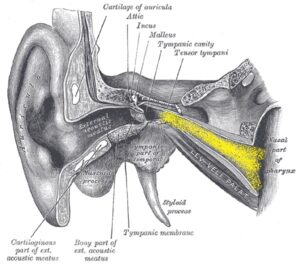
Milder ET symptoms may present with a pressure feeling in the ears, fluctuating or muffled hearing, problems with airplane flights or scuba diving (or even on very high building elevators). Many of these patients are OK at ground level but once you put the ears to the test with quick altitude change, quick pressure change, or a sinus infection the ears get swamped in and pain or infection may ensue – we refer this uncomfortable condition as a “barochallenge” symptom.
Dilation of the eustachian tube was tried decades ago but unsuccessful mostly due to poor surgical instruments at the time. However recently with advancing balloon technology we now have a good procedure, often done in the office, that will dilate the Eustachian tube soft structures to improve air and pressure clearance in the middle ear. Medicare and insurances are slowly catching up to this procedure and beginning to cover it. you may see this referred to as “Eustachian Tube Balloon Dilation” or ETBD.

Tuboplasty is a more broad term referred to surgically treating the doorway of the eustachian tube in the back of sinuses – the “torus tubarius“. This region is sometimes excessively bulky or impacted by the nearby adenoid pad and acts to seal off an otherwise-normal eustachian tube. Various techniques are used to debulk some of the redundany inflammatory tissue that many patients have here impacting eustachian tube clearance.
Eustachian tube dilation is a means to not only stretch a narrow ET passage, but actually reduce the submucosal inflammation cells in the tube, what researchers believe is the true reason the procedure lasts. Reducing inflammation in sinus and ear conditions is extremely important in many of the conditions we treat as Otolaryngologists. Part of the evaluation for these conditions should include allergy evaluation, CT imaging, and usually a trial of a simple nasal corticosteroid spray.
A nasal endoscopic exam while the patient is swallowing or speaking can help to see the size, shape and dynamic function of the torus tubarius and the eustachian tube itself. Along with symptoms and ear pressure testing we will be able to set up the best treatment plan. Many patients benefit from both ETBD and tuboplasty together.
Patients with barochallenge, whether from plane flights or scuba may benefit the most from ET balloon dilation and tuboplasty. Recurring adult ear infections is another useful condition. Some patients benefit from a traditional ear tube placed at the same time especially if inflammation has settled back in the middle ear space already.

